Specific Heat Capacity of Copper
The specific heat capacity for copper is 385 JkgC Delta E_t mcDelta theta. Or use the CtrlF function to find what you are looking for.

Dublin Schools Lesson Specific Heat
Paraffin for example has very large molecules and thus a high heat capacity per mole but as a substance it does not have remarkable heat capacity in terms of volume mass or atom-mol which is just 141 R per mole of atoms or less than half of most solids in.

. With our money back guarantee our customers have the right to request and get a refund at any stage of their order in case something goes wrong. An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energyMost electric motors operate through the interaction between the motors magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motors shaft. Heat capacity is an extensive propertyThe corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity found by dividing the heat capacity of an object.
If youd like to learn more about the specific heat of water at the molecular level. Specific heat capacity is the most useful quantity available from DSC because it is directly related to sample properties and according to eqns 15 directly linked to stability and order. Specific heat or specific heat capacity is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics.
The specific heat capacity is the heat or energy required to change one unit mass of a substance of a constant volume by 1 C. Below this table is an image version for offline viewing. Specific heat of products like wet mud granite sandy clay quartz sand and more.
Table of Specific Heat Capacities. Comparing this with values in Table T4 our experimental specific heat is closest to the value for copper 039 Jg C so we identify the metal as copper. Water has a high specific heat capacityit absorbs a lot of heat before it begins to get hot.
Nevertheless often only heat flow rate as obtained from a single sample measurement is presented. For comparison sake it only takes 385 Joules of heat to raise 1 kilogram of copper 1C. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin JK.
You may not know how that affects you but the specific heat of water. Q c p m dt 1 where. Specific Heat Capacity of Chemical Elements.
Definition of Specific heat capacity revealed that it is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 kilogram of any substance by 1 kelvin. The specific heat tells us how difficult it is to heat the given bodySubstances with low specific heat change their temperature easily whereas high ones require much more energy delivered to achieve identical effect. Molar C Jmol K.
The intensive properties c v and c p are defined for pure simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy uT v and enthalpy hT p respectively. Hence its derived SI unit is J kg1 K1. Specific heat or specific heat capacity is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics.
Specific heats and molar heat capacities for various substances at 20 C Substance. Ice -10 C 205. C in calgm K or Btulb F.
The difference can come from the temperature at which has been measured the specific heat capacity. In order to cause an equivalent temperature change in a mass of copper the same amount of heat will need to be applied 108. Specific heat of Copper is 038 Jg K.
C is the specific heat of a material JgK. Specific Heat Capacity of Metals Table Chart. Copper Specific heat capacity of Copper.
Specific heat or specific heat capacity is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. 2 kg of carbon steel is heated from 20 o C to 100 o C.
Materials Specific Heat Capacity of Metals Table Chart. Please scroll down the compounds are sorted alphabetically. The specific heat also called specific heat capacity is the measure of the heat energy that a substance in a unit quality absorbs or releases when the.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius JkgC. The energy required to heat a product can be calculated as. This is a much higher value than that of most other substances which makes water exceptionally good at regulating temperature.
The table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials and when applicable the molar heat capacity. In contrast copper has a specific heat capacity of 039 J. A specific heat capacity calculator is functioned to deliver the outcomes along with standardized units.
T 2 T 1 is the temperature difference before and after heating or cooling K. Specific Heat Capacity Examples. Material JkgK BtulbmF JkgC kJkgK Aluminium 887 0212 887 0887 Asphalt 915 021854 915 0915 Bone 440 0105 440 044 Boron 1106 0264 1106 1106 Brass 920.
How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of 3 kg of copper by 10C. List of thermal conductivities. Specific heat is a property of substance the so-called material constant.
Specific heat capacity depends only on the kind of substance absorbing or releasing heat. C in Jgm K. Specific Heat Capacity Unit.
Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Volume. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor but operates. The specific heat of copper is 385 Jkg K.
Gallium Specific heat. The formula is. Generally the most constant parameter is notably the volumetric heat capacity at least for solids which is around the value of 3 megajoule per cubic meter per kelvin.
Facebook Instagram Youtube Twitter. Q is the heat absorbed or released by a material J. The specific heat is the amount of heat energy per unit mass required to raise the temperature by one degree CelsiusThe relationship between heat and temperature change is usually expressed in the form shown below where c.
Q heat required kJ c p specific heat kJkg K kJkg C dt temperature difference K C Example - Heating Carbon Steel. M is the mass of a material g. If the sample is converted to heat by keeping its volume constant the actual heat produced by this process is known as Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Volume.
Water has a specific heat capacity of 418 J or 1 caloriegram C. Constantan is a coppernickel alloy consisting usually of 55 copper and 45 nickel and specific minor amounts of additional elements to achieve precise almost constant values. These condensers use tubes that are usually made of stainless steel copper alloys or titanium depending on several selection criteria such as thermal conductivity or.
Specific heat capacity of Copper. Heat Capacity - The amount of heat required to change the temperature of a. This means that it takes 4200 J to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1C.
The specific heat capacity of materials ranging from Water to Uranium has been listed below in alphabetical order. Also it depends on external conditions. It is an intensive propertythe type but not the amount of the substance is all that matters.
What is the specific heat capacity value of copper.

Which Metal Heats Up Fastest Aluminum Copper Or Silver Chemdemos

Can Anyone Suggest A Material With The Highest Specific Heat Capacity Higher Than Water

What Is The Formula For Specific Heat Capacity A Plus Topper
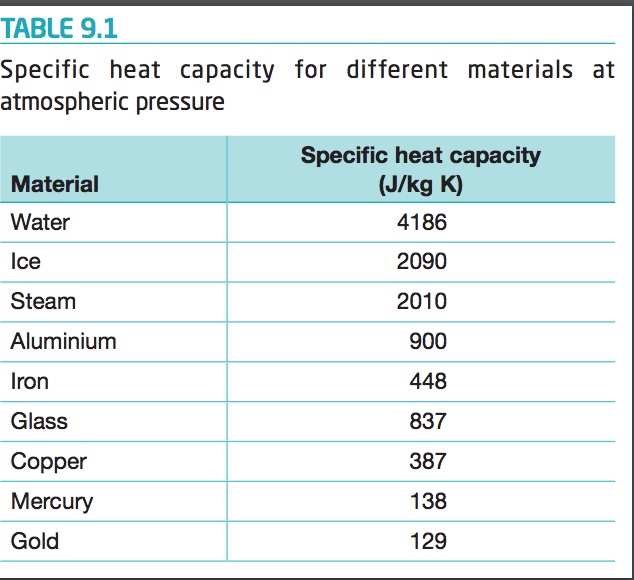
Solved Table 9 1 Specific Heat Capacity For Different Chegg Com
0 Response to "Specific Heat Capacity of Copper"
Post a Comment